(9)lim _(xarrow 0)dfrac (sqrt {1+5x)-sqrt (1-3x)}({x)^2+2x} .
题目解答
答案
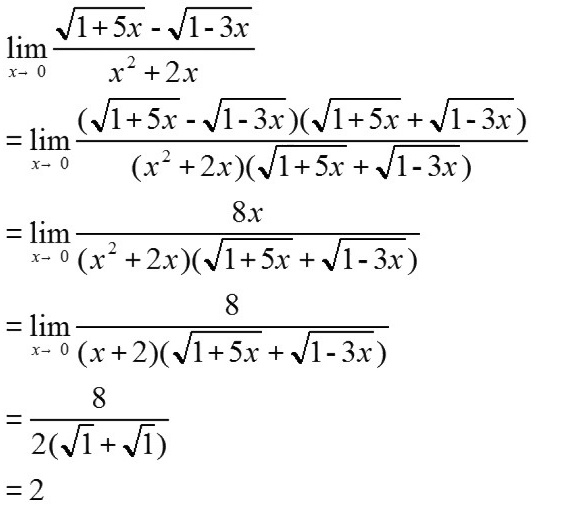
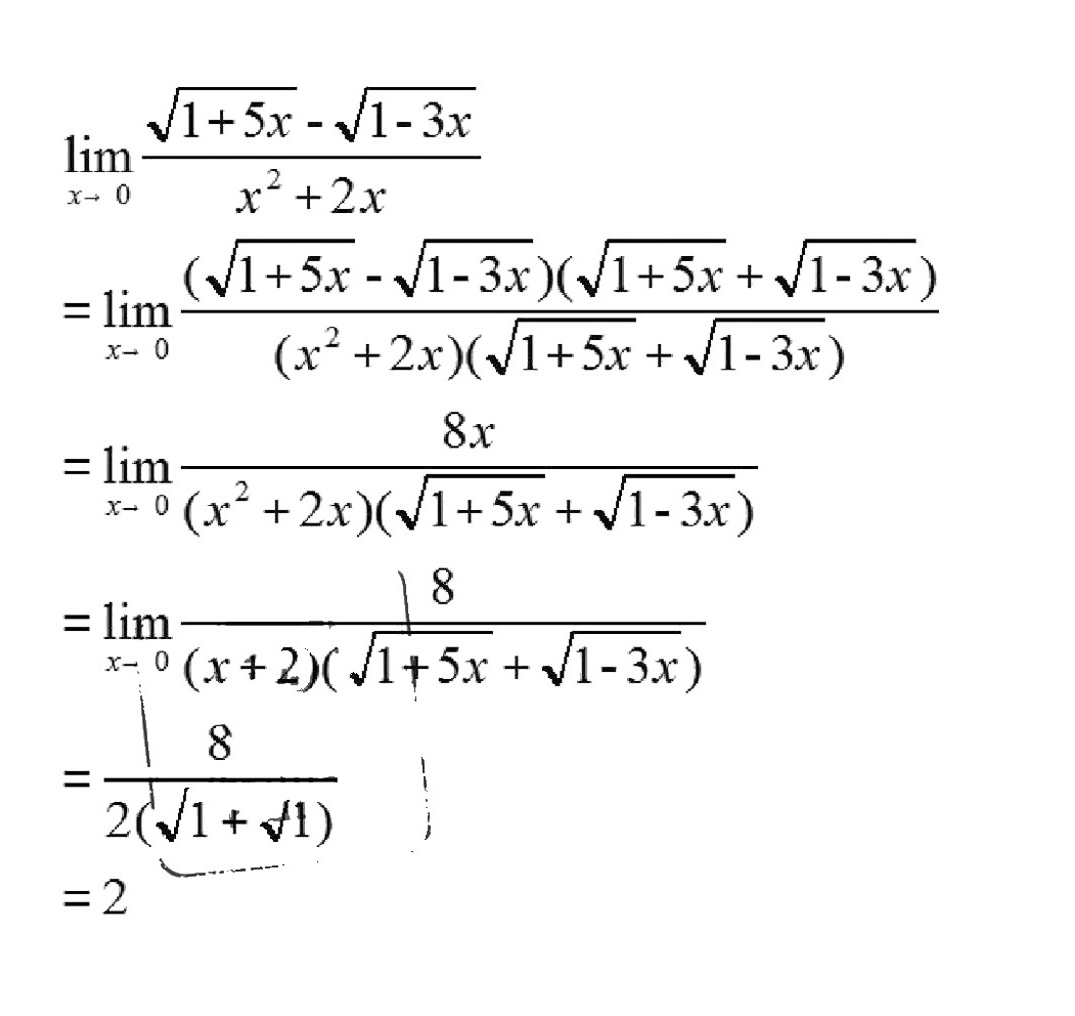
解析
考查要点:本题主要考查极限的计算,特别是处理根号差的技巧。关键在于通过有理化分子消除根号,将复杂表达式转化为可约分的形式,从而简化计算。
解题思路:
- 识别不定式类型:当$x \to 0$时,分子和分母均趋近于0,属于$\dfrac{0}{0}$型不定式。
- 有理化分子:通过乘以共轭根式,将分子转化为多项式,消除根号差。
- 约分简化:约去公共因子$x$,将表达式进一步化简。
- 代入求极限:直接代入$x=0$计算最终结果。
步骤1:有理化分子
分子为$\sqrt{1+5x} - \sqrt{1-3x}$,乘以共轭根式$\sqrt{1+5x} + \sqrt{1-3x}$:
$\begin{aligned}\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {\sqrt {1+5x}-\sqrt {1-3x}}{{x}^{2}+2x} &= \lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {(\sqrt {1+5x}-\sqrt {1-3x})(\sqrt {1+5x}+\sqrt {1-3x})}{({x}^{2}+2x)(\sqrt {1+5x}+\sqrt {1-3x})} \\&= \lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {(1+5x)-(1-3x)}{({x}^{2}+2x)(\sqrt {1+5x}+\sqrt {1-3x})} \\&= \lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {8x}{({x}^{2}+2x)(\sqrt {1+5x}+\sqrt {1-3x})}.\end{aligned}$
步骤2:约分简化
分母提取公因子$x$,分子分母约去$x$:
$\begin{aligned}&= \lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {8x}{x(x+2)(\sqrt {1+5x}+\sqrt {1-3x})} \\&= \lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {8}{(x+2)(\sqrt {1+5x}+\sqrt {1-3x})}.\end{aligned}$
步骤3:代入求极限
当$x \to 0$时,$\sqrt{1+5x} \to 1$,$\sqrt{1-3x} \to 1$,代入得:
$\begin{aligned}&= \dfrac{8}{(0+2)(\sqrt{1}+\sqrt{1})} \\&= \dfrac{8}{2 \times 2} = 2.\end{aligned}$